
ABSTRACT
This research attempts to formulate key aspects of design methodological framework which coalescing with fabrication role to build artifacts as part of the creative design process.
When the main question of architecture field is about “Target of architectural design”, comprehensive response would be concentrated on building the physical, factual and tangible phenomenon of that. This answer gives ride to another question that: “How it could be possible to reach to design production? “This matter propounds the importance and exigency of focus on choosing “Process based design” as the main approach.
As the reason of the digital contemporary era potentials and also, existence of complexity in forms, functions and management of most projects, absolutely, Choosing different approach in proportion of past , is necessary . All these conditions need a holistic view to design problems and cause to integrity of all parts of design fabrication process.
This approach to matter defines the parametric view, inherent to contemporary architecture context. Thus, composition of parametricism with characters of digital era , in according to the use of CAD(computer aided design ) and CAM( computer aided manufacturing) capabilities in design and fabrication / construction process , can lead to the regularity and computational inspiration in design process . Rule - bound and pattern based design can prepare the range of variant scales of models and prototypes which can test every matter of fabrication problems and eventually, materialize real world scale construction.
During the spiral process of design, expressions of fabrication play the virtual role of generating the design ideas according to some models of rapid prototyping. Actually, the reason of integrity in design fabrication process is the existence of joint language between variant design software and digital techniques and tools of fabrication like LCs and RPs
This methodology of thinking about design fabrication create the integrity needed between spiral process of design fabrication and it’s so many feedbacks with sequential construction process .The result of this happening , make a connection of academic architectural pedagogy and profession of this field . So, concentrating on design fabrication and fabricating design which completely considering the matter of construction and constructability, describe integrity of design process.
In correspondence with all explained , In this method of design research specially in educational part , so many problems which always are ignored and neglected in academic years of learning architecture like “ Details ”,” Materials ”, “assemblies techniques ”and some tools and techniques related to them , become highlighted as the content of research should be explored and evaluated.
In this research, a digital design fabrication method is introduced. The DDF method is the two stages process of working that integrates generative computing and RP in to one process. Thus , together ,they support a process to generate diverse candidate artifacts as solutions to design problems. This method demonstrates a process of design situated between conceptual design and real world construction.
Key Terms: Parametrisicm / Integrated Design / Process based design / Pattern based design /Design fabrication and fabricating design / Construction and Constructability / Tools and techniques of fabrication, Construction / Digital design fabrication






Final Thesis
Tehran University of Arts
School of Architecture
July 2011
Theoretical Part :
THE ROLE OF FABRICATION IN DESIGN PROCESS
Practical Part:
TEHRAN DESIGN & FABRICATION CENTER
Advisor: Prof. Mostafa Kiani
Fundamental Structure of Research
Parametricism
Parametricism is a mature style. That the parametric paradigm is becoming pervasive in contemporary architecture and design is evident for quite some time. There has been talk about versioning, iteration and mass customization etc. for quite a while within the architecture avant-garde discourse. The fundamental design that has come to the fore in this tendency has already been formulated at the beginning of the 1990s with the key slogan of “continuous differentiation”. Since then there has been both a widespread, even hegemonic dissemination of this tendency as well as a cumulative buildup of virtuosity, resolution and refinement within it. This development was facilitated by the attendant development of parametric design tools and scripts that allow the precise formulation and execution of intricate correlations between elements and subsystems. The shared concepts, computational techniques, formal repertories, and tectonic logics that characterize this work are crystalizing into a solid new hegemonic paradigm for architecture. One of the most pervasive current techniques involves populating modulated surfaces with adaptive components. Components might be constructed form multiple elements constrained/cohered by associative relations so that the overall component might sensibly adapt to various local conditions. As they populate a different iated surface their adaptation should accentuate and amplify this differentiation. This relationship between the base component and its various instantiations as different points of insertion in the “environment” is analogous to the way a single geno-type might produce a differentiated population of phenol-types in response to divers environmental conditions.
Patrik Schumacher, London 2008,
Presented and discussed at the Dark Side Club, 11th Architecture Biennale, Venice 2008

Holistic View to the Research
Main Keywords
Algorithmic View of Research Context

Integrated Design
Integrated design is a collaborative method for designing buildings which emphasizes the development of a holistic design.
Conventional building design usually involves a series of hand-offs from owner to architect, from builder to occupant. This path does not invite all affected parties into the planning process, and therefore does not take into account their needs, areas of expertise or insights. In some cases, using the conventional method, incompatible elements of the design are not discovered until late in the process when it is expensive to make changes. In contrast, the integrated design process requires multidisciplinary collaboration, including key stakeholders and design professionals, from conception to completion. Decision-making protocols and complementary design principles must be established early in the process in order to satisfy the goals of multiple stakeholders while achieving the overall project objectives.
In addition to extensive collaboration, integrated design involves a “whole building design” approach. A building is viewed as an interdependent system, as opposed to an accumulation of its separate components (site, structure, systems and use). The goal of looking at all the systems together to is make sure they work in harmony rather than against each other.
Integrated design has evolved in conjunction with the rise of multidisciplinary design firms and sustainable design. It frequently begins with a charrette or eco-charrette, an intensive design workshop, in which many stakeholders gather to set goals and identify strategies for achieving the desired outcomes. (Wikipedia)
Evaluation of Digital Tools and Techniques in Design Fabrication Process
Integrated Design Fabrication - CAD/ CAM Rules


MAIN RESEARCH DIAGRAMS
THEORETICAL PART:
THE ROLE OF FABRICATION IN DESIGN PROCESS
RACTICAL PART :
TEHRAN DESIGN & FABRICATION CENTER

Definition of Design Project

What is the definition of Design Problem?
Why this Matter is selected for Design Project?
The way of Responsivity to some imposed Forces and Ignoreing the others


Looking for Optimum Solutions in Design Process

Types of Diagrams Implemented in Design Process

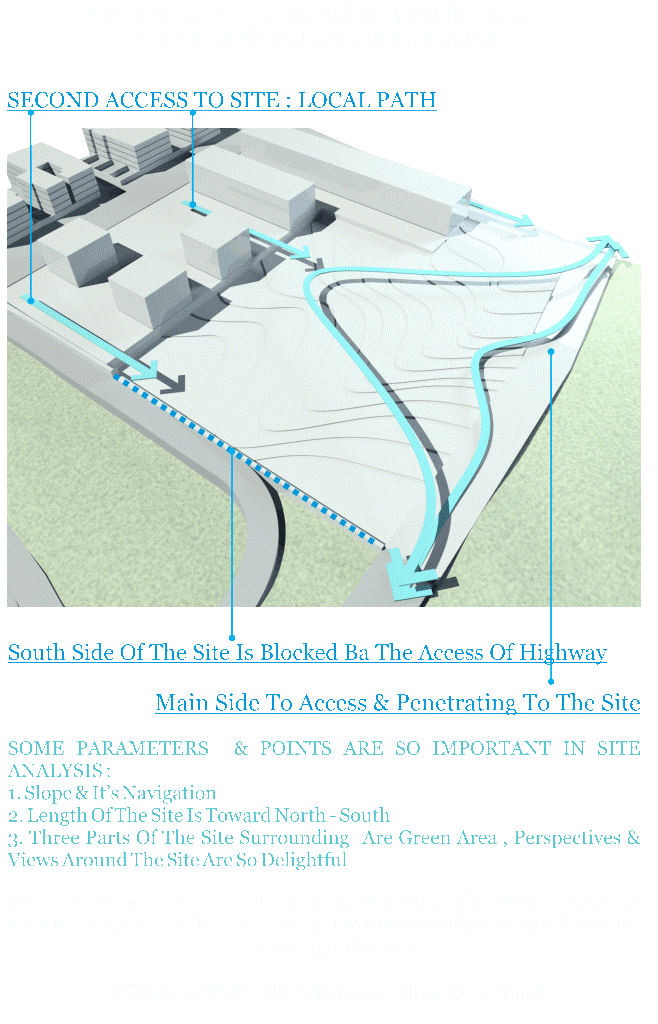
SITE ANALYSIS

Site Accesses
Site Views

Theoretical View to Combination and Composition of MASS - VOID
ROTATION create FOUR OPEN SPACE identically different with each other

FORM and ORIENTATION of the building will create PUBLIC , SEMI PUBLIC , SEMI PRIVATE, PRIVATE open spaces witch every one of them special FUNCTION and SENSE
Top View - Skin of Building
Perspective View - Skin of Building
Private Space -
For Gathering and Rest - for Students and Staffs
Public Space -
Defined by Main Entrance to the Site
Semi Public - Semi Private Space -
Open Exhibition and Showing Place for Students' Projects

Functional Level:



Continuous Surface that in response to the reaction of imposed forces, will transform to identically different spaces .
Basic point in design concept:
Continuous Surface inherently has the Potential of INTERNAL & EXTERNAL Spaces composition
This surface is the second skin of the facade which pulls itself toward the inside of the building .In this way creates two open terraces and then continuesits path completely inside of the building by TRANSFORMING in to the large INTERNAL VOID designed in the process
Flexibility In Design:
RESPONSIVITY to all forces imposed on the FORM of Building
Flexibility In Design:
RESPONSIVITY to all forces imposed on the FORM of Building
DESIGN FABRICATION and FABRICATING DESIGN
FABRICATING DESIGN :
CONSTRUCTION CUBIC NET OF COLUMN & BEAM as the Main Structure
SKIN of the project , According to Digital Fabrication Theories
FABRICATION TECHNIQUES :
CONTOUR : Parallel Section Regularity In relationship between components
POLYGONAL TESSELLATION : The way of TESTING CONSTRUCTABILITY of Design Process
Usage of TRIANGULAR TESSELLATION:
Making 3Dimensional Space frame Come Out of PLANAR REGULAR COMPONENT
FABRICATION TOOLS : LASER CUTTER OF CNCs
The Tools Are Categorized In 2Dimensional Digital Fabrication Techniques
LC Techniques of Digital Fabrication Techniques lead DESIGN PROCESS to Real World Scale Construction
METHOD OF FABRICATION :
They all involved extraction of 2 dimensional , planar components from geometrically complex surfaces or solids comprising the buildings from which of these strategies is used . Depends on what is being defined tectonically structure , envelope a combination of the two .





The way of Responsivity to some imposed Forces and Ignoreing the othi




AUTO CAD DRAWINGS in 2D section views


Small Scale Physical Modeling -Form Declaration - Fabricated by Laser Cutter



Small Scale Model Fabricated by LC - Central Void Presentation
Small Scale Physical Modeling of Generic Form Fabricated by Laser Cutter
Integrated - Parametric Digital Design Fabrication Process
Focus on the Role of GC in :Integrated - Parametric Digital Design Fabrication Process


Constructability and Construction in :Integrated - Parametric Digital Design Fabrication Process


